

The charges will, in general, oscillate slightly out of phase with respect to the driving electric field. The group index can be written in terms of the wavelength dependence of the refractive index asĪt the microscale, an electromagnetic wave's phase velocity is slowed in a material because the electric field creates a disturbance in the charges of each atom (primarily the electrons) proportional to the permittivity of the medium.
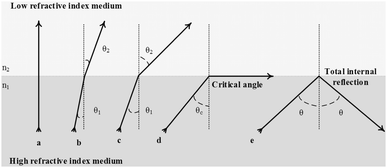
This value should not be confused with n, which is always defined with respect to the phase velocity. Sometimes, a "group velocity refractive index", usually called the group index is defined: This does not contradict the theory of relativity, which holds that no information-carrying signal can ever propagate faster than c, because the phase velocity is not the same as the group velocity or the signal velocity. near absorption resonances, and for X-rays), n will actually be smaller than one. This number is typically greater than one: the higher the index of the material, the more the light is slowed down (see Cherenkov radiation). Therefore, if v is the phase velocity of radiation of a specific frequency in a specific material, the refractive index is given by The speed of all electromagnetic radiation in vacuum is the same, approximately 3×10 8 meters per second, and is denoted by c. Since the phase velocity is lower in the second medium (v 2 < v 1), the angle of refraction θ 2 is less than the angle of incidence θ 1 that is, the ray in the higher-index medium is closer to the normal.

Refraction of light at the interface between two media of different refractive indices, with n 2 > n 1. Provided the waveform is not distorted significantly during propagation, it is the group velocity that represents the rate that information (and energy) may be transmitted by the wave, for example the velocity at which a pulse of light travels down an optical fiber. The group velocity is the rate that the envelope of the waveform is propagating that is, the rate of variation of the amplitude of the waveform. The phase velocity is defined as the rate at which the crests of the waveform propagate that is, the rate at which the phase of the waveform is moving. This has practical technical applications, such as effective mirrors for x-rays based on total external reflection. Contrary to a widespread misconception, n may be less than 1, for example for x-rays. For most materials, μ r is very close to 1 at optical frequencies, therefore n is approximately. Where ε r is the material's relative permittivity, and μ r is its relative permeability. air at a standardized pressure and temperature) have been common. It is most commonly used in the context of light with vacuum as a reference medium, although historically other reference media (e.g. The refractive index, n, of a medium is defined as the ratio of the phase velocity, c, of a wave phenomenon such as light or sound in a reference medium to the phase velocity,, in the medium itself:
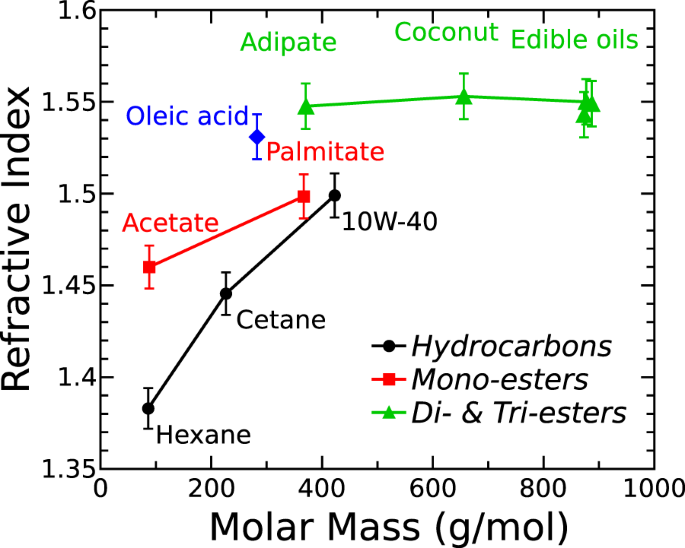
Second, light reflects partially from surfaces that have a refractive index different from that of their surroundings. First, light rays change direction when they cross the interface from air to the material, an effect that is used in lenses. Two common properties of glass and other transparent materials are directly related to their refractive index. For example, typical soda-lime glass has a refractive index of 1.5, which means that in glass, light travels at times the speed of light in a vacuum. The refractive index (or index of refraction) of a medium is a measure for how much the speed of light (or other waves such as sound waves) is reduced inside the medium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
